With always-on e-commerce becoming a reality of business, the requirement to manage a bigger number of SKUs with fewer errors, and the demand for quicker responses, warehouses must scale up and meet the standards of an automated, efficient, and intelligent warehouse. It is predicted a surge in digital transformation will result in fundamental changes to the way warehouses operate in the next 2 to 10 years.
A survey done by the MHI Annual Industry Report shows that 80% of respondents feel that the industry’s dominant model will be the digital supply chain within the next 5 years. It is already the dominant model for 20%.
There are 7 specific aspects of digital warehousing that look toward the future, and these will turn warehouse digitalization into reality.
- Warehouse Mobility Solutions
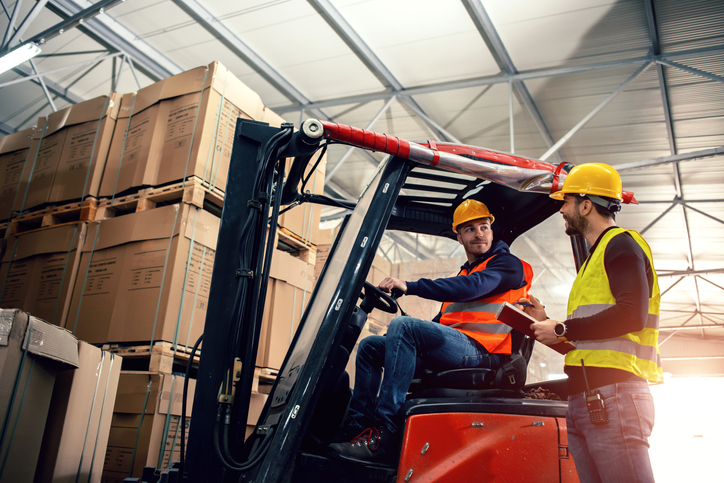
A key step forward in obtaining warehouse efficiency has been the transition from desktop computers to mobile devices and smartphones. Apps and devices nowadays substantially reduce walking time and enable warehouse employees to access data and work on the go outside as well as within a warehouse.
Smartphones not only liberate warehouse clerks from deskbound activities but also add new functionality to standard workstations. Mobile warehouse solutions are able to deliver the computational power and operational efficiency that warehouse operators require.
The advantages of functionality like personal assistants, tracking, imaging (video and pictures), videoconferencing, cloud integration, and face/voice recognition, open new transformational frontiers that these technologies can deliver to warehousing operations.
Warehouse mobility is a very secure area to invest in providing it is strategically aligned with operational requirements and well-planned. - Increased Interconnectivity and Real-Time Data Gathering
The supply chain and warehouse systems of the future will be transparent. Blockchain has the potential to play a key role in achieving this at every level. Blockchain technology offers the functionality to distribute information securely and fast, thereby making real-time data exchange for warehouses transparent and efficient.
Blockchain is not complete without another key technology: the Internet of Things (IoT). This ecosystem consists of sensory devices (e.g. for temperature, humidity, and location) that are connected via digital networks. These sensors collect real-time data and transmit it without human intervention.
Combined, these technologies provide real-time visibility and seamless collaboration among processes and chain partners, leading to effective, efficient, and highly evolved operating models. - Machine Learning and Smart Analytics
Warehouses play a key role in increasing customer satisfaction and are expected to predict product demand effectively, by making better use of the resources available. This has resulted in the demand for accurate forecasting and decision-making rising.
An ever-increasing number of warehouse managers are now looking at interpreting data trends to not only optimize asset utilization and warehouse capacity but also to anticipate stocks.
Predictive analytics plays a big role in this. Predictive analytics uses statistical techniques like data mining, big data, and predictive modeling to make predictions about the future by analyzing historical trends.
When used with artificial intelligence (AI), predictive analytics can be very effective for not only optimizing the warehouse as a whole, but also to increase operational efficiency, replenishing inventory, and recommending optimized inventory levels. - Autonomous Guided Vehicles
Although AGVs (Autonomous Guided Vehicles) are not widely adopted yet, they promise to revolutionize the way cargo is transported both outside and inside warehouses as potential substitutes for forklifts.
Drone technology will likely disrupt the warehousing industry. Drones are economical and safe when used to locate cargo, conduct inventory and cycle counting, and perform stock-taking operations.
A drone fitted with barcode scanners, sensors, cameras, or RFID technology can even reach the innermost spaces of a warehouse. They can also manage inventory and complete checks in less than 30% of the time required to do it manually.
AGVs can also move goods in the warehouse, and this contributes to inventory management operations and speeds up the picking process. - Robotics and Automation
Although warehouse automation is already actively being used in the industry, it still forms a big part of the future digital transformation. Robotics and automation simplify manual tasks with increased efficiency and much less cost and time. It is expected robotics will become more human-like in the areas of skill, sensing, memory, and affinity for learning without having to be programmed for specific skills (AI). Automation is an indispensable technology without which warehouses will not likely survive in the future. - The Technology-People Connection
One of the aspects of a modern digitized warehouse is the interconnection between warehouse technology and people. This is done via wearables. This type of technology provides warehouse managers and clerks access to a broad range of real-time information, irrespective of their physical constraints, environment, and location.
Wearables are small computers that are attached to the user’s head, wrist, or any other part of their body. Devices like voice-enabled devices, augmented reality, and smart glasses are becoming increasingly popular as a means of establishing effective system interaction.
This results in superior safety, improved information flow, a decrease in error rates, increased service levels, and greater visibility at lower operating costs.
Wearables help in optimizing efficiency in processes like receiving, order picking, high-value asset handling, handling, safety, workforce training, and cycle counting. - Inventory Management in Real Time
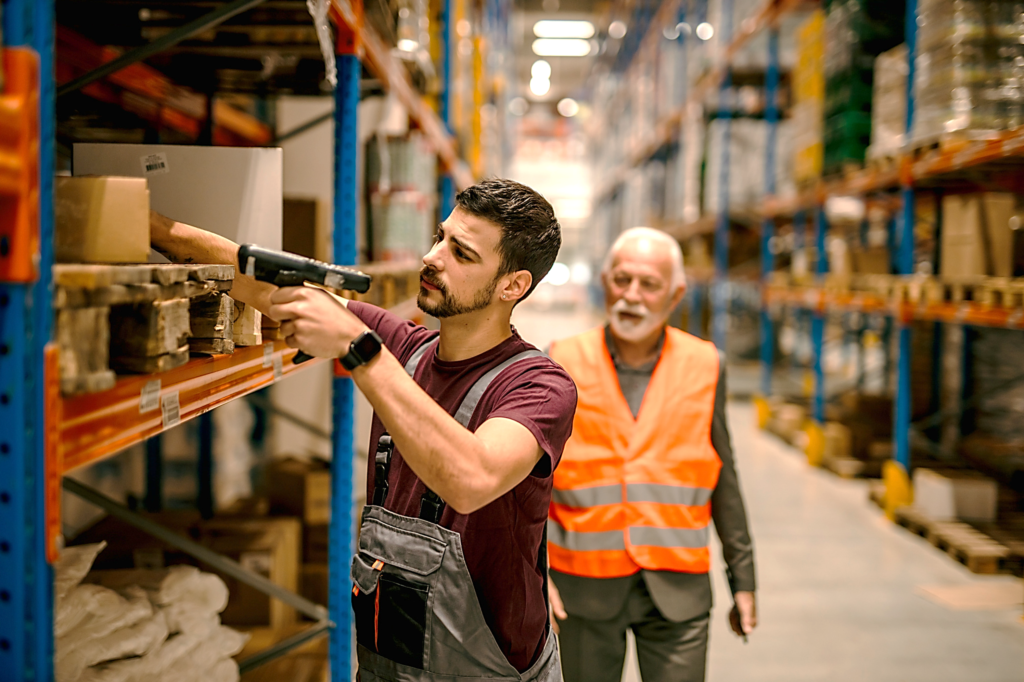
Heavy pressure is continuously being exerted on warehouse managers for improved inventory management. They need more control and visibility of inventory. Automatic identification systems like GPS, RFID, smart sensors, etc., provide not only end-to-end inventory visibility but also operational intelligence via the data collected by the sensors during processes.
Conclusion
Digitalization of warehouses is a reality that the warehousing industry should embrace if it wants to sustain its business and thrive amidst increasing market pressures and competition. The smart warehouse, which at the moment only seems like a disruptive force, will likely become the norm within the next 10 years.